
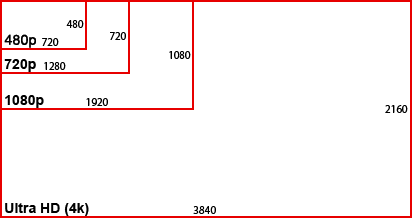
Ultra HD TV, also referred to as 4k, UHD, and Ultra HD is a video format with a resolution of 3840 x 2160 (8.3 megapixels) that is 4-times the Full HD standard of 1920 x 1080p (2.1 megapixels). Current HDTV standards also fall into two lower video resolutions that include 720p and 1080i, but those formats contain either fewer lines of resolution (720p) or are “interlaced” rather than progressive (1080i).
4k Ultra HD resolution was defined on Oct. 17, 2012, when the CEA (Consumer Electronics Association) announced the term Ultra HD (Ultra High Definition) would be used for displays with a video resolution of 3840 x 2160. But in most cases, consumer electronics manufacturers refer to Ultra HD sets also as 4k TVs, as the term is used more widely to describe the technology.
It’s interesting to note that in the film industry 4k has a slightly different definition for 4k. The Digital Cinema Initiatives (DCI) established the SMPTE 428-1 standard that defines several 4k resolutions that include 4096 × 2160 (full frame), 3996 × 2160 (flat crop), and 4096 × 1716 (CinemaScope crop), all with slightly different aspect ratios.
In home applications, 4k is more accurately described as 3840 x 2160 (2160p) which fits into the 16 x 9 aspect ratio of HD and 4k Ultra HD TVs and projectors. But, in looking at the numbers you will the width does not quite make 4,000 (why 4k DCI is called 4k).
The next jump in video resolution is 8k UHD at 7680 x 4320 (33.2 megapixels), which is 16-times the current HDTV standard. See 4k/8k TVs on Amazon
Here is a chart that illustrates the different format sizes.
Also Read:
What is 4k Ultra HD TV?
Is 4k resolution the same as 2160p?
What is HDR?
